Plotting in azmpdata
E. Chisholm
12/4/2020
Source:vignettes/plotting_azmpdata.Rmd
plotting_azmpdata.Rmd## casaultb/azmpdata status:## (Package ver: 0.2019.0.9100) Up to date## (Data ver:2021-01-14 ) Up to date## azmpdata:: Indexing all available monthly azmpdata...##
## Attaching package: 'dplyr'## The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
##
## filter, lag## The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
##
## intersect, setdiff, setequal, unionIntroduction
The purpose of this vignette is to demonstrate how to plot data which is pulled from the azmpdata package. We show brief examples of various plotting methods including base plot, and ggplot2. We also review how to recreate default plots from the gslea package which has similar functionality to azmpdata but contains Gulf and Quebec region data products.
The Data
We will use sample data from the azmpdata package for each example. Data can be called using
## station year integrated_chlorophyll_0_100 integrated_nitrate_0_50
## 1 HL2 1999 67.87150 85.3821
## 2 HL2 2000 52.27038 153.5603
## 3 HL2 2001 68.29393 149.7280
## 4 HL2 2002 47.71381 103.0353
## 5 HL2 2003 96.58182 150.9685
## 6 HL2 2004 66.68268 126.5663
## integrated_nitrate_50_150 integrated_phosphate_0_50
## 1 914.6475 25.47386
## 2 1052.4824 30.74438
## 3 852.9537 37.94380
## 4 986.5876 31.48064
## 5 1043.8373 29.25722
## 6 859.2595 27.55872
## integrated_phosphate_50_150 integrated_silicate_0_50
## 1 95.37123 133.7420
## 2 106.72167 188.2529
## 3 115.91301 165.8859
## 4 112.68214 112.0497
## 5 105.77327 178.2837
## 6 99.75733 159.4061
## integrated_silicate_50_150 sea_surface_temperature_from_moorings
## 1 1028.1987 NA
## 2 1027.9558 NA
## 3 848.0259 NA
## 4 905.5085 NA
## 5 972.7365 NA
## 6 832.2479 NA
## temperature_in_air cruiseNumber longitude latitude pressure temperature_0
## 1 NA <NA> NA NA NA NA
## 2 NA <NA> NA NA NA NA
## 3 NA <NA> NA NA NA NA
## 4 NA <NA> NA NA NA NA
## 5 NA <NA> NA NA NA NA
## 6 NA <NA> NA NA NA NA
## temperature_90 integrated_sea_temperature_0_50 integrated_salinity_0_50
## 1 NA NA NA
## 2 NA NA NA
## 3 NA NA NA
## 4 NA NA NA
## 5 NA NA NA
## 6 NA NA NA
## integrated_sigmaTheta_0_50
## 1 NA
## 2 NA
## 3 NA
## 4 NA
## 5 NA
## 6 NABase plot
Using base R to create plots can often be the simplest way for a novice to explore a dataset.
If we wanted to create a simple plot of a variable over time, it might look like this
plot(df$year, df$temperature_in_air, xlab = 'Year', ylab = 'temperature_in_air')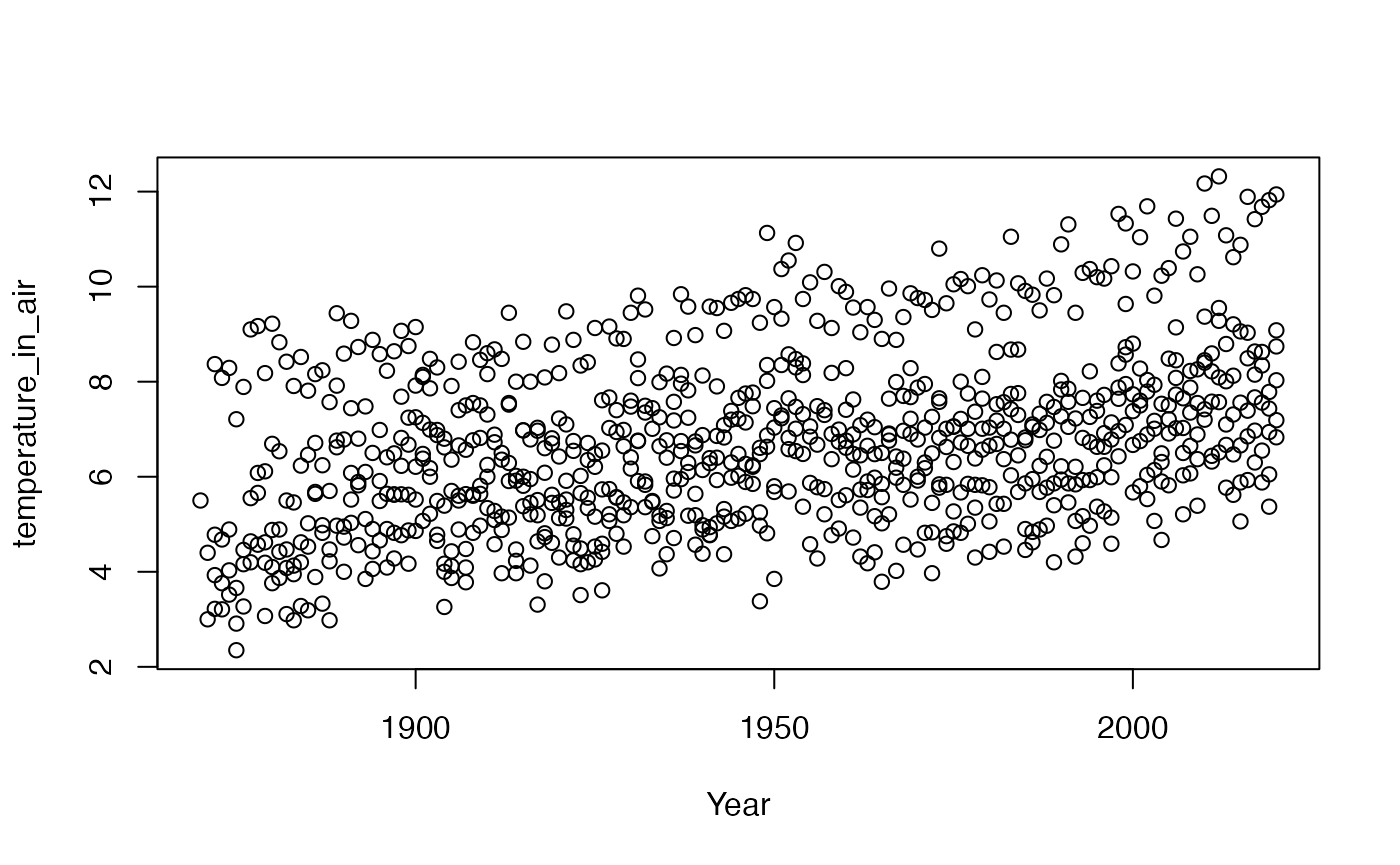
Obviously there are many more advanced plots that can be made using base plot but we leave these up to the individual users to explore.
ggplot2
Using ggplot2 can give great simple exploratory plots, using a different ‘grammar’.
If a user wanted to compare different variables over time, ggplot2 has functions which make this very simple.
p <- ggplot(data = df) +
geom_line(aes(x = year, y = temperature_in_air, colour = 'air_temperature'), show.legend = TRUE) +
geom_point(aes(x = year, y = sea_surface_temperature_from_moorings, colour = 'sea_surface_temperature_from_moorings'), show.legend = TRUE)+
labs(y = 'degrees C' ) +
scale_color_manual(name = "variables",
breaks = c('air_temperature', 'sea_surface_temperature_from_moorings'),
values = c('air_temperature' = 'red', 'sea_surface_temperature_from_moorings' = 'blue'))
print(p)## Warning: Removed 4 row(s) containing missing values (geom_path).## Warning: Removed 1030 rows containing missing values (geom_point).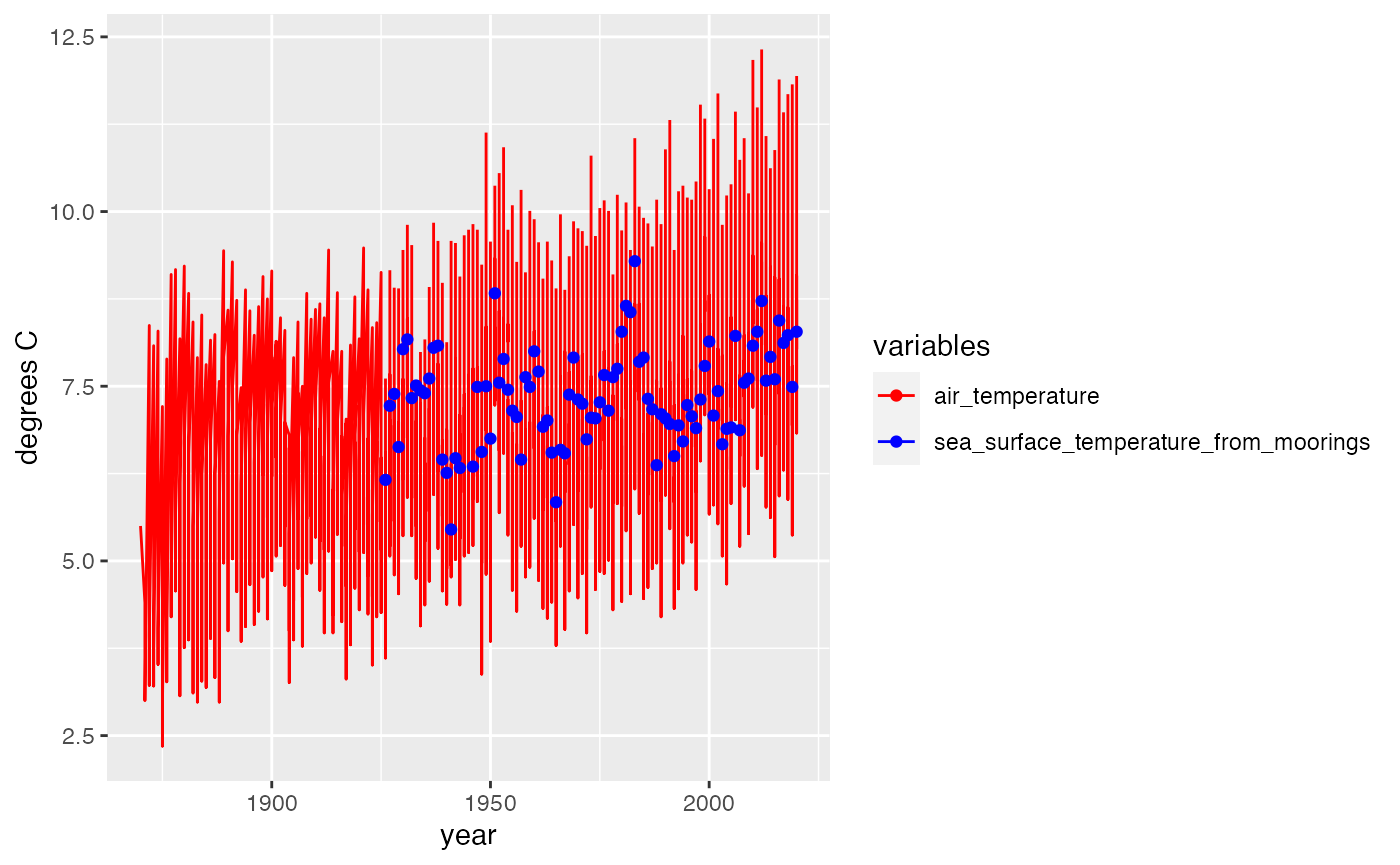
The next two examples contain generic code that could be modified to plot any dataframe (of the same time scale).
Another common plotting task would be to plot the annual means of a given dataframe. This method is fairly generic and could be used for any annual dataset.
df_data <- get('Derived_Annual_Broadscale') # get data
variable <- 'temperature_at_sea_floor' # select variable to plot
# check for metadata and seperate
metanames <- c('year','area', 'section', 'station' )
meta_df <- names(df_data)[names(df_data) %in% metanames]
group <- meta_df[meta_df != 'year']
df_data <- df_data %>%
dplyr::select(., all_of(meta_df), all_of(variable) ) %>%
dplyr::rename(., 'value' = all_of(variable) ) %>%
dplyr::rename(., 'group' = all_of(group))
# set x-axis
x_limits <- c(min(df_data$year)-1, max(df_data$year)+1)
x_breaks <- seq(x_limits[1], x_limits[2], by=1)
x_labels <- x_breaks
# set y-axis
y_limits <- c(min(df_data$value, na.rm=T) - 0.1*mean(df_data$value, na.rm=T),
max(df_data$value, na.rm=T) + 0.1*mean(df_data$value, na.rm=T))
# plot data
p <- ggplot2::ggplot() +
# plot data - line
ggplot2::geom_line(data=df_data,
mapping=ggplot2::aes(x=year, y=value, col = group),
size=.5) +
# plot data - dots
ggplot2::geom_point(data=df_data,
mapping=ggplot2::aes(x=year, y=value, col = group),
size=1) +
# set coordinates system and axes
ggplot2::coord_cartesian() +
ggplot2::scale_x_continuous(name="Year", limits=x_limits, breaks=x_breaks, labels=x_labels, expand=c(0,0)) +
ggplot2::scale_y_continuous(name="", limits=y_limits, expand=c(0,0))
# customize theme
p <- p +
ggplot2::theme_bw() +
ggplot2::ggtitle(paste(group, variable, sep=" : " )) +
ggplot2::theme(
text=ggplot2::element_text(size=8),
axis.text.x=ggplot2::element_text(colour="black", angle=90, hjust=0.5, vjust=0.5),
plot.title=ggplot2::element_text(colour="black", hjust=0, vjust=0, size=8),
panel.grid.major=ggplot2::element_blank(),
panel.border=ggplot2::element_rect(size=0.25, colour="black"),
plot.margin=grid::unit(c(0.1,0.1,0.1,0.1), "cm"))
print(p)## Warning: Removed 277 row(s) containing missing values (geom_path).## Warning: Removed 397 rows containing missing values (geom_point).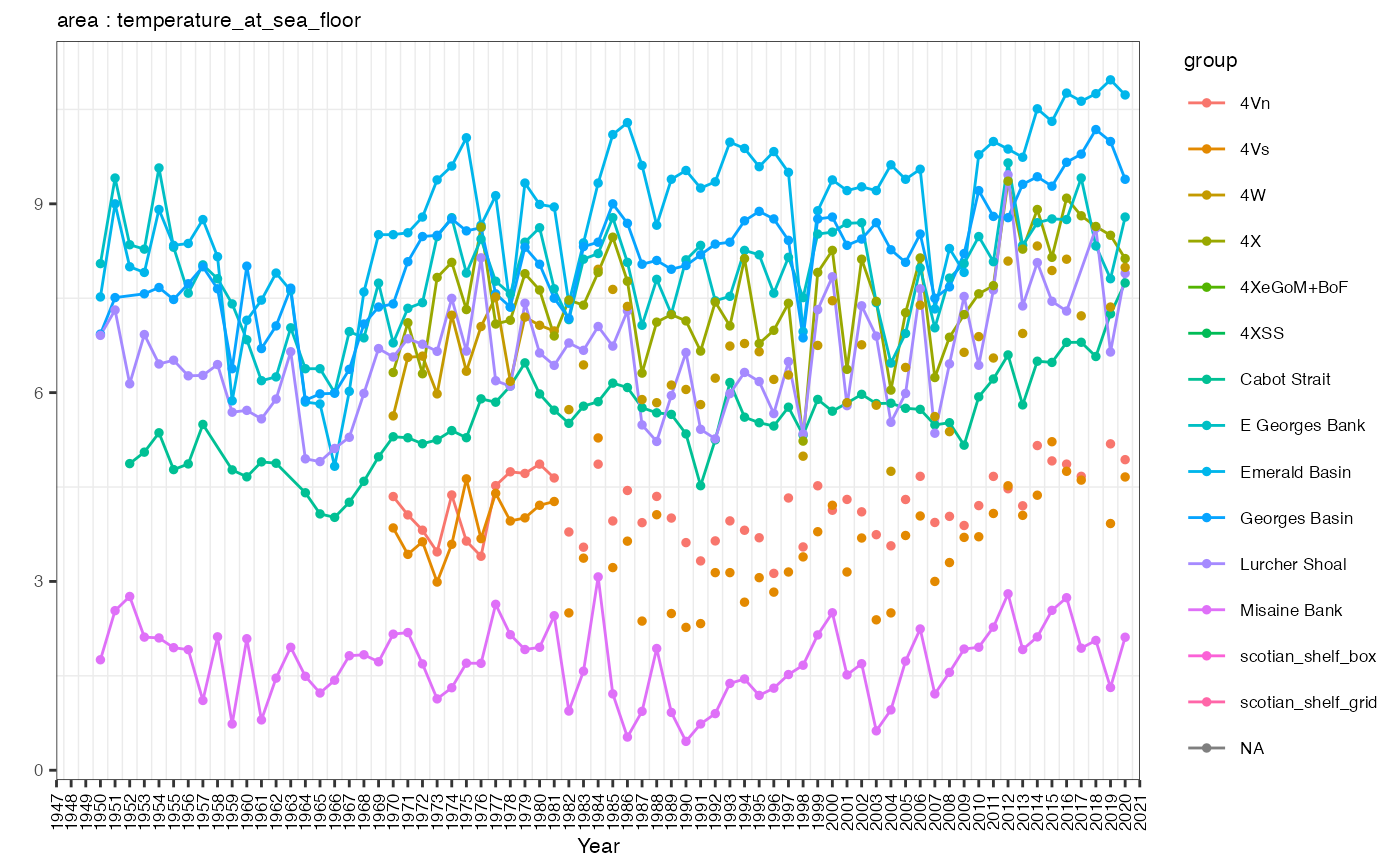
A user may also want to plot a timeseries. This method is also fairly generic and could be modified to plot any Occupations dataset.
df_data <- get('Discrete_Occupations_Stations') # get data
variable <- 'chlorophyll' # choose variable to plot
# check for metadata
metanames <- c('year', 'month', 'day', 'area', 'section', 'station' )
meta_df <- names(df_data)[names(df_data) %in% metanames]
group <- meta_df[!meta_df %in% c('year', 'month', 'day')]
df_data <- df_data %>%
dplyr::select(., all_of(meta_df), all_of(variable) ) %>%
dplyr::rename(., 'value' = all_of(variable) ) %>%
dplyr::rename(., 'group' = all_of(group)) #TODO some dataframes do not have groups!?
# prepare data
df_data <- df_data %>%
tidyr::unite(date, year, month, day, sep="-", remove=F) %>%
dplyr::mutate(year_dec=lubridate::decimal_date(lubridate::ymd(date))) %>%
dplyr::select(year, year_dec, value, group)
# set x-axis
x_limits <- c(min(df_data$year), max(df_data$year)+1)
x_breaks <- seq(x_limits[1]+.5, x_limits[2]-.5, by=1)
x_labels <- x_breaks-.5
# set y-axis
y_limits <- c(min(df_data$value, na.rm=T) - 0.1*mean(df_data$value, na.rm=T),
max(df_data$value, na.rm=T) + 0.1*mean(df_data$value, na.rm=T))
## set shaded rectangles breaks
df_rectangles <- tibble::tibble(xmin=seq(x_limits[1], x_limits[2], by=2),
xmax=seq(x_limits[1], x_limits[2], by=2)+1,
ymin=y_limits[1], ymax=y_limits[2])
# plot data
p <- ggplot2::ggplot() +
# plot shaded rectangles
ggplot2::geom_rect(data=df_rectangles,
mapping=ggplot2::aes(xmin=xmin, xmax=xmax, ymin=ymin, ymax=ymax),
fill="gray90", alpha=0.8) +
# plot data - line
ggplot2::geom_line(data=df_data,
mapping=ggplot2::aes(x=year_dec, y=value, col = group),
size=.5) +
# plot data - dots
ggplot2::geom_point(data=df_data,
mapping=ggplot2::aes(x=year_dec, y=value, col = group),
size=1) +
# set coordinates system and axes
ggplot2::coord_cartesian() +
ggplot2::scale_x_continuous(name="Year", limits=x_limits, breaks=x_breaks, labels=x_labels, expand=c(0,0)) +
ggplot2::scale_y_continuous(name="", limits=y_limits, expand=c(0,0))
# customize theme
p <- p +
ggplot2::theme_bw() +
ggplot2::ggtitle(paste(group, variable, sep=" : " )) +
ggplot2::theme(
text=ggplot2::element_text(size=8),
axis.text.x=ggplot2::element_text(colour="black", angle=90, hjust=0.5, vjust=0.5),
plot.title=ggplot2::element_text(colour="black", hjust=0, vjust=0, size=8),
panel.grid.major=ggplot2::element_blank(),
panel.border=ggplot2::element_rect(size=0.25, colour="black"),
plot.margin=grid::unit(c(0.1,0.1,0.1,0.1), "cm"))
print(p)## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_rect).## Warning: Removed 26 row(s) containing missing values (geom_path).## Warning: Removed 6060 rows containing missing values (geom_point).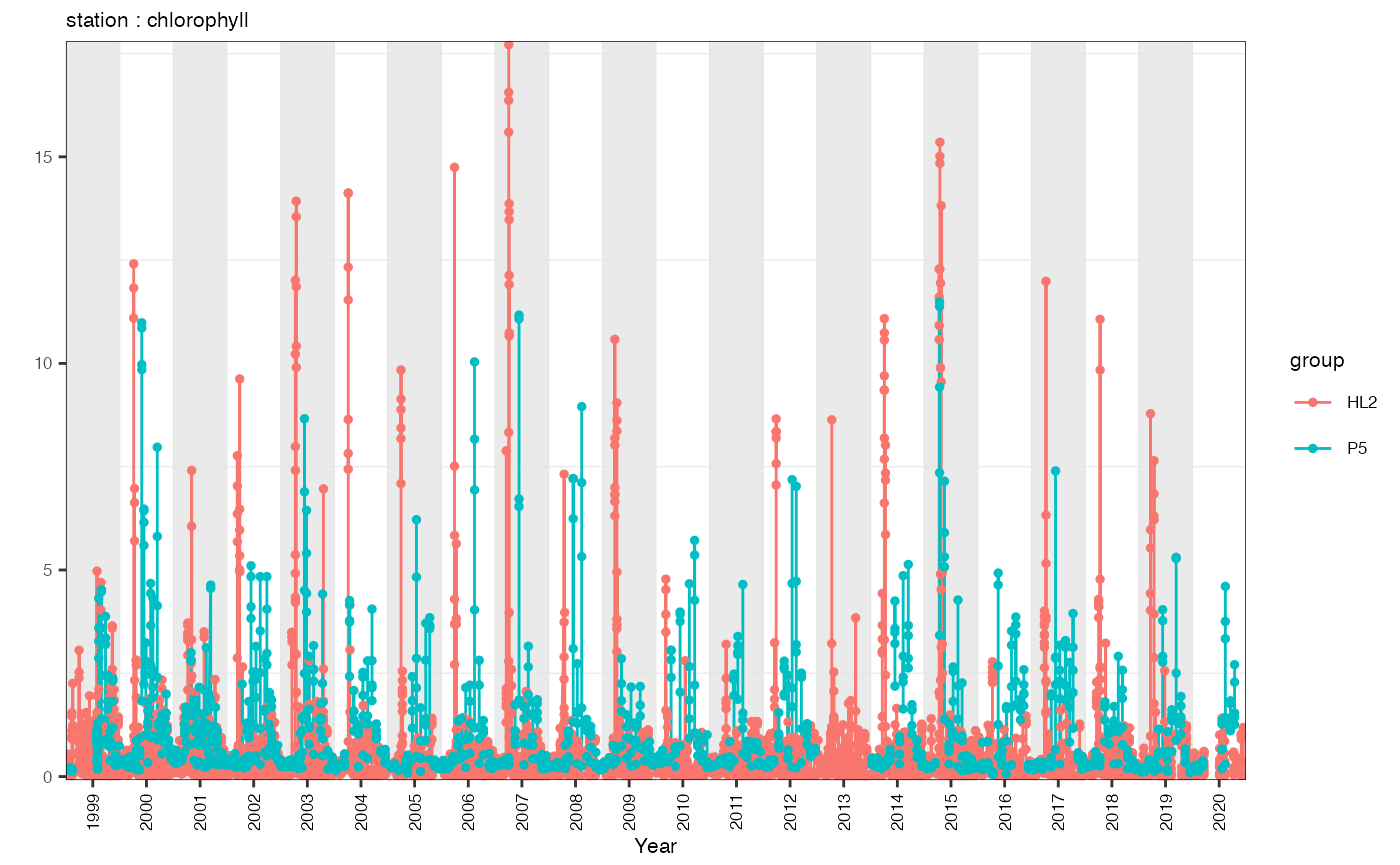
gslea
gslea was a package developed to support ecosystem approach research in the Gulf Region. It contains a plotting function EA.plot.f() which can be replicated using azmpdata.
Note these plots may appear very small in the notebook format.
dat <- get('Derived_Annual_Stations')
actual_EARs <- unique(dat$station) # get regions to plot
dat_only <- dat[,!names(dat) %in% c('station', 'year', 'cruiseNumber', 'longitude', 'latitude', 'pressure')] # isolate data variables to plot (not metadata)
no_plots <- length(dat_only)*length(actual_EARs) # calculate number of plots ot be displayed
# set par info based on number of plots (max 25 per page)
if(no_plots > 25) {par(mfcol = c(5, 5), mar = c(1.3,2,3.2,1), omi = c(.1,.1,.1,.1), ask = T)}
if(no_plots <= 25){par(mfcol = c(length(dat_only), length(actual_EARs)), mar = c(1.3,2,3.2,1), omi = c(.1,.1,.1,.1))}
counter <- 1
for(i in actual_EARs){ # loop through regions
ear_dat <- dat[dat$station == i,]
for(ii in 1:length(dat_only)){ # loop by variables
var_dat <- data.frame('value' = ear_dat[[names(dat_only)[[ii]]]], 'station' = ear_dat$station, 'year' = ear_dat$year) # get only one variable for one region
if(!is.na(diff(range(var_dat$value)))){ # if all values are NA skip over plotting
# plot
if(nrow(var_dat) < 1) plot(0,
xlab = "", ylab = "",
xaxt = "n", yaxt = "n",
main = paste("Station",i,names(dat_only)[[ii]]))
if(nrow(var_dat) > 0) plot(var_dat$year, var_dat$value,
xlab = "", ylab = "",
main = paste("Station",i,names(dat_only)[[ii]]))
}
}
counter <- counter+1
}
# set par info
par(mfcol = c(1,1), omi = c(0,0,0,0), mar = c(5.1, 4.1, 4.1, 2.1), ask = F)